biology eoc study guide
Welcome to the Biology EOC Study Guide, a comprehensive resource designed to help students master key biology concepts and prepare effectively for their exams. This guide provides a structured approach to learning, covering essential topics, study strategies, and practice questions to ensure success. By organizing content to align with the EOC exam format, it offers a user-friendly pathway to achieving academic goals in biology.
1.1 What is the Biology EOC Exam?
The Biology End-of-Course (EOC) exam is a standardized test assessing students’ understanding of fundamental biological concepts. It evaluates knowledge across key topics such as cell structure, genetics, evolution, and ecosystems. Designed to measure mastery of high school biology curriculum, the exam includes multiple-choice questions and may incorporate performance tasks. The EOC exam is a critical assessment for many students, often influencing academic progress and graduation requirements. It aims to ensure students demonstrate proficiency in scientific inquiry, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills essential for success in advanced studies. Preparing for this exam requires a thorough review of core concepts and the development of effective test-taking strategies.
1.2 Importance of the Biology EOC Exam
The Biology EOC exam holds significant importance as it measures a student’s grasp of essential biological principles and their ability to apply this knowledge. High scores can enhance academic records, contributing to college admissions and scholarship opportunities. Additionally, it serves as a benchmark for schools to evaluate teaching effectiveness and curriculum alignment. For students, success on the EOC exam fosters confidence in their scientific understanding and prepares them for advanced coursework. Overall, the exam plays a pivotal role in assessing academic readiness and promoting educational growth, making it a crucial milestone in a student’s high school career.
1.3 How to Use This Study Guide Effectively
To maximize the benefits of this Biology EOC Study Guide, students should adopt a structured and consistent approach. Begin by reviewing each section thoroughly, ensuring understanding of key concepts before moving on. Utilize the practice questions to test knowledge and identify areas needing improvement. Incorporate active learning techniques, such as summarizing notes and engaging in study groups, to reinforce retention. Additionally, allocate specific time slots for each topic to maintain a balanced study schedule. Regularly review and analyze mistakes to refine understanding. By following these strategies, students can efficiently navigate the guide and achieve their academic goals with confidence and preparedness. Regular practice and review are essential for long-term retention and exam success.

Cell Structure and Function
This section explores the fundamental components of cells, including organelles, transport mechanisms, and the cell cycle. Understanding these concepts is crucial for mastering cellular biology and related processes.
2.1 Overview of Cell Organelles
Cell organelles are specialized structures within cells that perform specific functions essential for cellular survival and activity. The nucleus serves as the control center, housing DNA. Mitochondria generate energy through cellular respiration, while ribosomes synthesize proteins. The endoplasmic reticulum processes proteins and lipids, and the Golgi apparatus modifies and transports them. Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes, breaking down waste and foreign substances. Chloroplasts, found in plant cells, conduct photosynthesis. Each organelle’s unique role contributes to the cell’s overall function, making their study vital for understanding cellular biology.
2.2 Cell Transport Mechanisms
Cell transport mechanisms are processes that allow molecules to enter or exit cells, maintaining homeostasis and enabling cellular functions. Passive transport, requiring no energy, includes diffusion (movement from high to low concentration) and osmosis (water diffusion). Active transport moves molecules against concentration gradients, using energy from ATP. Endocytosis and exocytosis involve vesicles transporting large molecules or particles. These mechanisms ensure proper nutrient uptake, waste removal, and communication between cells. Understanding them is crucial for grasping how cells interact with their environment and sustain life.
2.3 The Cell Cycle and Division
The cell cycle is a series of stages that cells undergo to grow, replicate, and divide. It consists of interphase, where the cell grows and prepares for division, and the mitotic phase, where the cell divides. During interphase, DNA replicates, and proteins are synthesized. Mitosis includes prophase (chromatin condenses), metaphase (chromosomes align), anaphase (sister chromatids separate), and telophase (nuclear envelope reforms). Cytokinesis follows, splitting the cytoplasm and forming two daughter cells. This process ensures genetic continuity and is vital for growth, repair, and reproduction. Understanding cell division is crucial for studying genetics and development, as errors can lead to abnormalities like cancer.
Genetics and Heredity
Genetics and heredity are fundamental concepts in biology, explaining how traits are passed from one generation to the next through DNA, genes, and inheritance patterns.
3.1 DNA Structure and Replication
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is a double-stranded helix made up of nucleotides, each containing a sugar, phosphate, and nitrogenous base; The sugar in DNA is deoxyribose, and the bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). DNA replication is a semi-conservative process where each strand serves as a template for a new complementary strand. This ensures genetic continuity, as each new DNA molecule retains one original strand. Understanding DNA structure and replication is crucial for grasping genetic inheritance and molecular biology concepts in the Biology EOC exam, as it forms the foundation of heredity and gene expression.
3.2 Mendelian Genetics and Inheritance Patterns
Mendelian genetics, established by Gregor Mendel, explores how traits are inherited through the transmission of genetic information. Key principles include the Law of Segregation and the Law of Independent Assortment. These laws explain how alleles (different forms of a gene) separate and recombine during gamete formation. Mendel’s studies on pea plants revealed dominant and recessive traits, demonstrating predictable inheritance patterns. Understanding these concepts is vital for analyzing Punnett squares, which predict offspring genotypes and phenotypes. This foundation in genetics is essential for success on the Biology EOC exam, as it underpins modern genetic principles and applications in heredity and biotechnology.
3.3 Modern Genetic Techniques and Biotechnology
Modern genetic techniques and biotechnology have revolutionized the field of biology, enabling precise manipulation of DNA and the development of innovative tools. Key technologies include polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for DNA amplification, gel electrophoresis for DNA separation, and CRISPR-Cas9 for gene editing. These methods allow scientists to modify organisms, produce recombinant proteins, and engineer crops with desirable traits. Biotechnology applications extend to medicine, agriculture, and environmental science, offering solutions such as disease-resistant plants and gene therapy. Understanding these techniques is crucial for the Biology EOC exam, as they highlight humanity’s ability to harness genetic knowledge for advancement. Ethical considerations also play a significant role in their application.
Evolution and Natural Selection
Evolution and natural selection are fundamental concepts in biology, explaining how species adapt and change over time through genetic variation and environmental pressures, driving diversity and survival.
4.1 Key Concepts in Evolution
Evolution is the scientifically supported theory that all species descend from common ancestors through gradual changes over time. Natural selection, genetic drift, mutation, and gene flow are key drivers. Mutation introduces genetic variation, while natural selection favors traits that enhance survival and reproduction. Genetic drift alters allele frequencies randomly, and gene flow transfers genes between populations. These mechanisms collectively shape biodiversity and adaptation. Understanding these concepts is crucial for grasping how life on Earth has diversified. This section explores these principles in depth, providing a foundation for analyzing evolutionary processes and their impact on ecosystems and species development.
4.2 Mechanisms of Natural Selection
Natural selection is a fundamental mechanism of evolution where populations adapt over generations. It begins with genetic variation within a population, such as differences in traits or characteristics. Environmental pressures then favor individuals with advantageous traits, enhancing their survival and reproductive success. These individuals pass their beneficial traits to their offspring, leading to an accumulation of adaptations. Over time, this process can result in the evolution of new species. Natural selection acts on existing variation and does not create new traits. For example, the peppered moth’s color shift during the industrial revolution illustrates how environmental changes drive selective pressures. Understanding this mechanism is essential for grasping evolutionary changes and biodiversity.
4.3 Evidence for Evolution
The evidence for evolution is vast and comes from multiple fields of study. Fossil records reveal a chronological progression of life forms, showing gradual changes over time. Comparative anatomy and embryology highlight similarities among species, suggesting common ancestry. Molecular biology demonstrates genetic relationships through DNA and protein comparisons. Biogeography explains species distribution patterns consistent with evolutionary history. Additionally, observable evolutionary changes in laboratory and natural settings, such as antibiotic resistance, provide direct evidence. These diverse lines of evidence collectively support the theory of evolution, offering a well-rounded understanding of how life has diversified on Earth over millions of years.
Ecology and Ecosystems
Explore the intricate relationships within ecosystems, focusing on energy flow, nutrient cycles, population dynamics, and community interactions. Understand how human activities impact biodiversity and environmental balance.
5.1 Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles
Energy flow in ecosystems follows a unidirectional path, beginning with producers who capture sunlight through photosynthesis. This energy is transferred to consumers, with only about 10% passing to each subsequent trophic level. Nutrient cycles, such as carbon, nitrogen, and water cycles, ensure the continuous availability of essential resources for living organisms. These cycles sustain life by recycling nutrients through ecosystems, maintaining balance and supporting biodiversity. Understanding these processes is crucial for grasping how ecosystems function and how human activities can impact them. This section delves into the mechanisms and importance of energy flow and nutrient cycling, providing foundational knowledge for ecology and conservation biology.
5.2 Population Dynamics and Community Interactions
Population dynamics involve the study of how population sizes change over time, influenced by factors such as birth rates, death rates, immigration, and emigration. These changes are shaped by environmental conditions, resource availability, and interactions with other species. Community interactions refer to the relationships between different species within an ecosystem, including predation, competition, mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism. These interactions play a crucial role in maintaining ecosystem balance and biodiversity. Understanding population dynamics and community interactions is essential for analyzing how ecosystems function and respond to environmental changes. This section explores these concepts in detail, providing insights into the complex web of life within ecosystems.
5.3 Human Impact on Ecosystems
Human activities have profoundly altered ecosystems worldwide, leading to environmental challenges such as deforestation, pollution, climate change, and biodiversity loss. Deforestation disrupts habitats and reduces carbon sequestration, while pollution contaminates air, water, and soil, affecting both flora and fauna. Climate change accelerates species extinction and disrupts ecological balances. Overexploitation of resources and invasive species further threaten ecosystem stability. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing sustainable practices and mitigation strategies. This section examines the various ways humans influence ecosystems and explores solutions to minimize these effects, ensuring a healthier planet for future generations. Addressing these issues requires a combination of scientific knowledge and responsible stewardship.
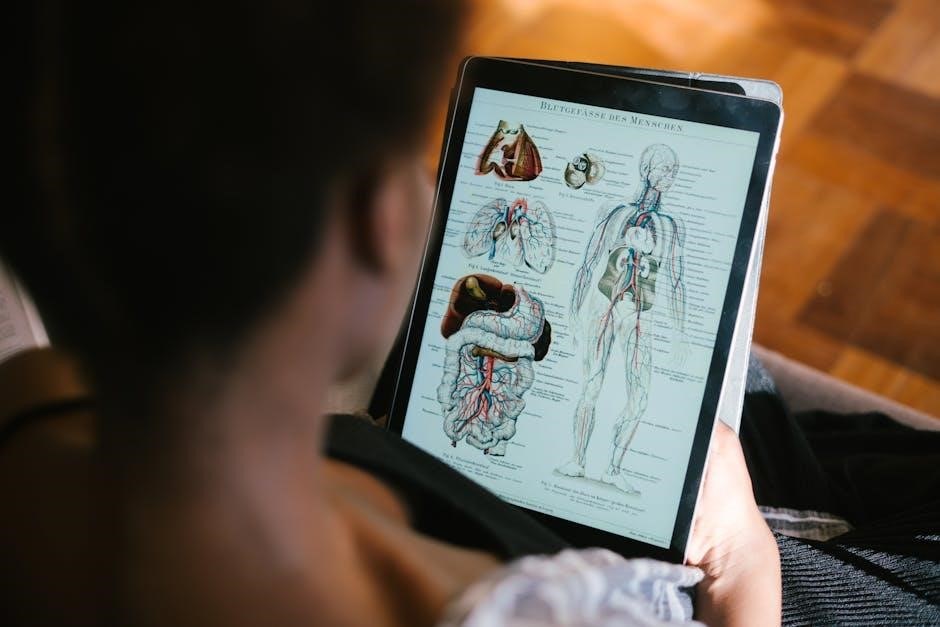
Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
This section explores the fundamental biomolecules, metabolic pathways, and molecular mechanisms underlying life. It delves into the chemistry of carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids, as well as enzyme functions and energy transformations through photosynthesis and cellular respiration, crucial for understanding biological systems and their applications in medicine and biotechnology.
6.1 Biomolecules: Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids
Biomolecules are the building blocks of life, essential for energy storage, structural support, and genetic information. Carbohydrates, such as sugars and starches, serve as the primary energy source for cells. Proteins, composed of amino acids, perform diverse functions, including enzyme catalysis and structural roles. Nucleic acids, like DNA and RNA, store and transmit genetic information. Understanding their structures, functions, and interactions is crucial for grasping biological processes. This section provides a detailed exploration of these biomolecules, their classifications, and their roles in maintaining life, preparing students for related questions on the Biology EOC exam.
6.2 Enzymes and Their Role in Biological Processes
Enzymes are biological catalysts, primarily proteins, that accelerate chemical reactions in cells. They bind to substrates, lowering activation energy and enabling reactions to occur efficiently. Essential for life, enzymes regulate metabolism, DNA replication, and signal transduction. Each enzyme has a specific active site, ensuring precise substrate binding. Factors like temperature, pH, and inhibitors can affect enzyme activity. Coenzymes and cofactors often assist enzymes in their functions. Understanding enzyme kinetics, types, and their roles in metabolism is vital for grasping biological processes. This section explores enzyme mechanisms, their importance in cellular functions, and how they drive essential biochemical pathways, preparing students for related EOC exam questions.
6.3 Photosynthesis and Respiration
Photosynthesis and respiration are critical biological processes that sustain life. Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts, where plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy, producing glucose and oxygen. This process relies on chlorophyll and light absorption. Respiration, occurring in mitochondria, breaks down glucose to release energy, producing ATP, carbon dioxide, and water. It includes glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain, with the latter producing the most ATP. Both processes are vital for energy conversion in cells. Understanding their roles, stages, and interconnections is essential for mastering cellular biology and related EOC exam questions.
Study Strategies for Success
Effective study strategies include active learning, organized note-taking, and regular review sessions. Prioritize understanding concepts, use flashcards, and practice past exam questions to reinforce knowledge retention.
7.1 Effective Note-Taking Techniques
Effective note-taking is crucial for retaining information and excelling in the Biology EOC exam. Use the Cornell Method to organize notes, ensuring key terms and concepts are highlighted. Summarize complex ideas in your own words to enhance understanding. Review notes within 24 hours of class and periodically thereafter to reinforce memory. Utilize bullet points, diagrams, and flowcharts to visually map out processes like cell division or photosynthesis. Prioritize active learning by engaging with material during lectures, asking questions, and relating new information to previous knowledge. Consistent and organized note-taking will help you master biology concepts efficiently and effectively for exam success.
7.2 Active Learning and Review Methods
Active learning and consistent review are essential for mastering biology concepts. Engage with material through self-quizzing, flashcards, and summarizing key points. Teach concepts to others to deepen understanding. Use spaced repetition to review notes over time, enhancing long-term retention. Incorporate practice questions to apply knowledge and identify weaknesses. Group study sessions can foster collaboration and clarify doubts. Additionally, create mnemonics or memory aids to remember complex processes like DNA replication. Regularly revisit and organize notes, linking new information to prior knowledge. Active learning strategies ensure a dynamic and effective approach to studying biology, making it easier to retain and recall information during exams.
7.3 Time Management for Exam Preparation
Effective time management is crucial for successful Biology EOC exam preparation. Create a study schedule that balances review, practice, and rest. Prioritize topics based on difficulty and importance, allocating more time to challenging areas. Break study sessions into manageable chunks, using techniques like the Pomodoro Technique to maintain focus. Set specific, achievable goals for each session and track progress. Incorporate regular breaks to avoid burnout and enhance retention. Use a planner or digital tool to organize tasks and deadlines. Regularly review and adjust your schedule to ensure alignment with exam requirements. Consistent, structured studying helps build confidence and reduces exam stress, ensuring you’re well-prepared for test day.

Test-Taking Tips and Tricks
Master strategies to excel on exam day. Read questions carefully, manage time wisely, and eliminate incorrect answers. Stay calm and use proven techniques to approach each question confidently.
8.1 Understanding Different Question Types
Understanding various question types is crucial for effective test preparation. The Biology EOC exam includes multiple-choice questions, short-answer responses, and possibly essay questions. Multiple-choice questions test factual recall and analytical skills, requiring careful reading to identify distractors. Short-answer questions assess your ability to explain concepts concisely; Essay questions evaluate in-depth knowledge and critical thinking. Familiarizing yourself with each format helps tailor your study approach. Practice each type to build confidence and improve time management. Recognizing question patterns enhances your ability to allocate time wisely during the exam, ensuring you address each section effectively.
8.2 Strategies for Multiple-Choice Questions
Mastering multiple-choice questions requires a strategic approach. Begin by carefully reading each question and identifying key terms. Eliminate obviously incorrect answers first to narrow down options. Pay attention to absolute words like “always” or “never,” as these often signal incorrect choices. Use the process of elimination to increase your chances of selecting the right answer. If unsure, make an educated guess based on prior knowledge; Skim through answer choices to spot similar options that might be distractors. Manage your time wisely, spending no more than 60 seconds on a single question. Practice under timed conditions to build speed and accuracy. This methodical approach will enhance your performance on multiple-choice sections of the exam.
8.3 Managing Test Anxiety
Test anxiety can significantly impact performance, but effective strategies can help mitigate it. Start by practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises or positive visualization, to calm your mind before and during the exam. Familiarize yourself with the test format to reduce uncertainty. Stay hydrated and eat a nutritious meal to maintain energy levels. Avoid cramming by ensuring consistent study habits leading up to the exam. Focus on what you can control, such as your preparation, rather than worrying about outcomes. Use positive self-talk to build confidence, and remind yourself of past successes. By managing anxiety, you can approach the test with clarity and confidence, ensuring your best performance.
Practice Questions and Review
This section provides a variety of practice questions to test your understanding of key biology concepts. Reviewing these questions helps identify strengths and areas needing improvement. Full-length practice tests simulate exam conditions, ensuring readiness. Use this section to refine your knowledge and build confidence for the EOC exam.
9;1 Sample Questions by Topic
This section offers a collection of sample questions organized by key biology topics, such as cell structure, genetics, and ecology. Each question is designed to assess your understanding of specific concepts and processes. By practicing these questions, you can identify areas where you need additional review and track your progress over time. The questions mirror the format and difficulty of the actual EOC exam, ensuring you are well-prepared for test day. Use these samples to reinforce your knowledge, develop problem-solving skills, and build confidence in tackling a variety of biological topics. Regular practice with these questions will help you approach the exam with clarity and precision.
9.2 Analyzing Mistakes and Improving
Analyzing mistakes is a crucial step in improving your understanding and performance. After completing practice questions or tests, review each incorrect answer to identify where you went wrong. Focus on understanding the underlying concept or process that led to the error. Use this insight to target weak areas in your study plan. Reflect on whether the mistake was due to a misunderstanding of the material, a misinterpretation of the question, or test-taking anxiety. Adjust your study strategies accordingly, such as spending more time on challenging topics or practicing time management. By addressing errors systematically, you can strengthen your knowledge and build confidence for the exam.
9.3 Full-Length Practice Tests
Full-length practice tests are an essential tool for simulating the actual exam experience. These tests mirror the format, timing, and content of the Biology EOC exam, helping you assess your readiness. By completing them under timed conditions, you can improve time management and reduce test anxiety. Regularly taking full-length practice tests allows you to identify knowledge gaps and track your progress over time. Reviewing your results helps pinpoint areas needing additional study. Use these tests to refine your strategies for tackling different question types and to build confidence in your abilities. Consistent practice with full-length tests is a proven way to achieve a higher score on the actual exam.

Additional Resources and References
Explore recommended textbooks, online platforms, and educational apps that complement your study guide. Utilize interactive simulations, video tutorials, and study groups to enhance your learning experience.
10.1 Recommended Textbooks and Websites
For in-depth learning, consider textbooks like Campbell Biology and Biology: The Core, which provide detailed explanations of key concepts. Online resources such as Khan Academy and Crash Course Biology offer video tutorials and practice questions. Websites like Quizlet and Mastering Biology are excellent for interactive flashcards and simulations. Additionally, ScienceDaily and PubMed offer current research articles to deepen your understanding of biological topics. These resources complement the study guide by offering diverse learning tools to reinforce your knowledge and prepare you effectively for the Biology EOC exam.
10.2 Online Tutoring and Study Groups
Enhance your learning with online tutoring platforms like Chegg Tutors and Varsity Tutors, which offer one-on-one guidance tailored to your needs. Join virtual study groups through platforms like Discord or Reddit communities, where you can collaborate with peers, share resources, and discuss challenging topics. These groups often host live sessions and Q&A forums, fostering a supportive environment for collective learning. Online tutoring provides flexibility and personalized attention, while study groups promote active engagement and peer-to-peer learning. Both resources complement the study guide by offering real-time interaction and collaborative problem-solving, helping you stay motivated and well-prepared for the Biology EOC exam.
10.3 Mobile Apps for Biology Review
Utilize mobile apps like Quizlet and Kahoot to enhance your biology review on-the-go. These apps offer interactive flashcards, practice quizzes, and games to make learning engaging. Khan Academy and Coursera provide video tutorials and structured courses to deepen your understanding of complex topics. Additionally, apps like Biology Dictionary and Cell & Biology offer detailed explanations and visuals for key concepts. Mobile apps are ideal for quick study sessions, allowing you to review anywhere, anytime. They complement this study guide by offering interactive and visual learning tools, ensuring you stay prepared and confident for the Biology EOC exam with accessible and flexible resources.